High Arch Foot Hurts
Overview
Arch pain is felt on the underside of your foot between the heel and ball. The purpose of the arch is to transfer your body weight from heel to toe, and pain is the result when the arch doesn?t function properly. Your foot actually contains two arches: the longitudinal arch which runs the length of your foot, and the transverse arch (also known as the metatarsal arch) which spans the width of your foot. There are 24 bones which create the arches and these bones are held together through their unique interlocking shapes and ligaments. The muscles and the plantar fascia (a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs from the heel to the toes) provide secondary support, and fat pads help to absorb impact and bear your weight. If any of these structures or their interaction are damaged or faulty, arch pain may occur. The most common cause of arch pain is plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the plantar fascia. You may also suffer arch pain if you have a structural imbalance in your foot or suffer from arthritis. But arch pain may also result from stepping on a rock or when someone steps on your foot. This force may cause an injury such as a bone fracture or damage to the supporting muscles, ligaments, or tendons underneath your foot.

Causes
There are many causes for a high arch (cavus) foot. In the United States, the most common cause for a high arch foot is a form of muscular dystrophy called hereditary sensorimotor neuropathy. Most people recognize this by the more commonly used name of Charcot Marie Tooth disease (CMT). This is a disease of the muscles and the nerves of the legs, and occasionally of the hands, in which certain muscles weaken while others retain their strength. The condition is transmitted as an autosomal dominant condition. This means that 50% of the offspring will statistically inherit the disorder. This is, however, just a statistic. In some families, all the children develop the condition while in others, none inherit it.
Symptoms
Arch pain symptoms could include any of the following, a dull, constant ache if the ligaments have been stretched, swelling or tenderness in the foot, redness or bruising in the event of a more serious injury, difficulty putting weight on the foot, sharp pain when the foot is turned or manipulated, tenderness when pressure is applied. Because the arch of the foot is such a complex structure, arch pain could be an indicator of several different types of injuries. Chronic illnesses such as arthritis could also cause arch pain, and depending on the cause or source of your pain, you may experience discomfort in a variety of different areas. Ask a doctor if you believe you may have injured your foot arch.
Diagnosis
In people with flat feet, the instep of the foot comes in contact with the ground when standing. To diagnose the problem, the health care provider will ask you to stand on your toes. If an arch forms,the flat foot is called flexible. You will not need any more tests or treatment. If the arch does not form with toe-standing (called rigid flat feet), or if there is pain, other tests may be needed, including a CT scan to look at the bones in the foot. MRI scan to look at the tendons in the foot. X-ray of the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are many different causes of and treatments for flat foot. The most important part of treatment is determining the exact flat foot type on an individual basis, and doing so early on. The main objective is to become educated on the potential problems, so that you can stop them before they start. Conservative treatment is often successful if initiated early. The old adage "a stitch in time saves nine" definitely applies to the human body, hopefully more figuratively than literally. Do not ignore what your common sense and your body are telling you. Yes, you can live without an arch, but never neglect a symptomatic foot. If you neglect your feet, they will make you pay with every literal step you take.
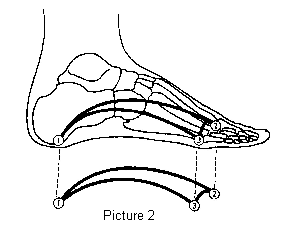
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be necessary in situations where the symptoms are likely to get worse over time, or when pain and instability cannot be corrected with external orthopedic devices. There are many types of surgical procedures, including cavus foot reconstruction, which can be performed to correct the foot and the ankle and restore function and muscle balance.
Prevention
Strap the arches into the anatomically correct positions with athletic tape and leave them like this for some time. If the fallen arches are an issue with the muscular structure, this may give the muscles an opportunity to strengthen. This is definitely not a fallen arches cure all the time but it can help prevent it more times than not. Ask a doctor or physical therapists to show you how to do this taping. Find shoes that fit. This may require that you get your foot measured and molded to ensure that the shoe will fit. Shoes that are too big, too tight or too short, may not directly cause the fallen arches, but they can assist with the damage to the area. These shoes should have thick cushioning inside and have plenty of room for your toes. Walk without shoes as much as possible. Shoes directly assist with weakening and distorting the arches of the feet so going without shoes can actually help strengthen your arches and prevent fallen arches. Walking on hard and bumpy surfaces barefooted makes the muscles in your feet strengthen in order to prevent injury. It is a coping mechanism by your body. Insert heel cups or insoles into the shoes that you wear the most. Many people wear uncomfortable shoes to work and these are the same shoes that cause their arches the most problems. Inserting the heel cups and insoles into these shoes can prevent fallen arches from occurring. Many people place these inserts into all their shoes to ensure support. Ask a medical professional, either your doctor or a physical therapist, about daily foot exercises that may keep the arches stronger than normal. Many times, you can find exercises and stretches on the Internet on various websites. Curling your toes tightly and rotating your feet will help strengthen your longitudinal arches. Relax your feet and shake them for a minute or so before you do any arch exercises. This will loosen the muscles in your feet that stay tight due to normal daily activities. Wear rigid soled sandals whenever possible to provide a strong support for your arches. Wooden soled sandals are the best ones if available. Walk or jog on concrete as much as you can. This will create a sturdy support for your arches. Running or walking in sandy areas or even on a treadmill, does not give rigid support. Instead, these surfaces absorb the step, offering no support for arches.
Stretching Exercises
Calf Stretching in Bed. As you may already know, the first few steps out of bed in the morning can be the worst of the day. Those first few steps can be enough to reaggravate your condition putting you into a cycle of inflammation and pain. The best way to help break that cycle is to stretch your calf before taking those first steps in the morning. When the muscles in your calf are tight, they pull on the heel bone, making your plantar fascia very taut and prone to injury. To help loosen those muscles, take a towel or belt and loop it around the ball of your foot. Keeping your leg straight, gently pull towards your body until you feel a stretch in the lower part of your leg. Hold that for 30 seconds and repeat up to 5 times before taking your first step out of bed. Plantar Fascia Stretching. Loosening up the tissues that are irritated probably makes sense to you, but you may not know how to do so. Luckily, there?s a very simple way. All you have to do is pull your toes up with your hand until you feel a stretch along the ball of your foot. You may feel the stretch anywhere from the ball of your foot to your heel. Holding this position for 30 seconds a few times can make a world of difference in your pain levels. Calf Stretching. I know, it probably seems like overkill, but stretching out the muscles in the lower leg is an integral step to recovery. There are two main muscles in the lower leg that attach to the heel, so we?ll work on stretching them both out. Stand against a wall and slide one leg back, pushing the heel down towards the floor (first picture). When you feel a stretch in the lower part of your leg, hold it for 30 seconds. After those 30 seconds are up, bend your knees until a deeper stretch is felt a bit lower in the leg (second photo). Again, hold this stretch for 30 seconds and repeat this until you?ve done it 3 times on each leg. Who doesn?t love a good massage? I suppose you could pay for someone to rub out the tissues in the bottom of your foot, but if you?re looking for a cheaper alternative, look no further than the humble tennis ball. Placing a tennis ball on the ground and gently rolling it under foot for a few minutes can help loosen up your plantar fascia, making it much less likely to become irritated. Put enough pressure on the ball to get a deep massage. You may feel some soreness, but back off if you feel any pain.Tennis Ball Massage While using the tennis ball is great for keeping things loose, sometimes it?s worth doing some icing at the same time for some inflammation control. Freezing a water bottle and rolling it under your foot for 10 minutes at the end of the day can be a very effective way to keep inflammation in check while staying loose. It might not be the most comfortable thing in the world, but ?Brrr? is better than ?Ouch? any day. One thing to keep in mind is that while these tips have been proven to work, they?re not an instant fix. It can take a few weeks of consistency with them before your pain levels begin to change. If you?re not seeing any improvement after making an honest effort, it may be time to look into some different treatment methods with your doctor such as formal PT, orthotics, a weight-loss plan, or others.
Arch pain is felt on the underside of your foot between the heel and ball. The purpose of the arch is to transfer your body weight from heel to toe, and pain is the result when the arch doesn?t function properly. Your foot actually contains two arches: the longitudinal arch which runs the length of your foot, and the transverse arch (also known as the metatarsal arch) which spans the width of your foot. There are 24 bones which create the arches and these bones are held together through their unique interlocking shapes and ligaments. The muscles and the plantar fascia (a broad band of fibrous tissue which runs from the heel to the toes) provide secondary support, and fat pads help to absorb impact and bear your weight. If any of these structures or their interaction are damaged or faulty, arch pain may occur. The most common cause of arch pain is plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the plantar fascia. You may also suffer arch pain if you have a structural imbalance in your foot or suffer from arthritis. But arch pain may also result from stepping on a rock or when someone steps on your foot. This force may cause an injury such as a bone fracture or damage to the supporting muscles, ligaments, or tendons underneath your foot.

Causes
There are many causes for a high arch (cavus) foot. In the United States, the most common cause for a high arch foot is a form of muscular dystrophy called hereditary sensorimotor neuropathy. Most people recognize this by the more commonly used name of Charcot Marie Tooth disease (CMT). This is a disease of the muscles and the nerves of the legs, and occasionally of the hands, in which certain muscles weaken while others retain their strength. The condition is transmitted as an autosomal dominant condition. This means that 50% of the offspring will statistically inherit the disorder. This is, however, just a statistic. In some families, all the children develop the condition while in others, none inherit it.
Symptoms
Arch pain symptoms could include any of the following, a dull, constant ache if the ligaments have been stretched, swelling or tenderness in the foot, redness or bruising in the event of a more serious injury, difficulty putting weight on the foot, sharp pain when the foot is turned or manipulated, tenderness when pressure is applied. Because the arch of the foot is such a complex structure, arch pain could be an indicator of several different types of injuries. Chronic illnesses such as arthritis could also cause arch pain, and depending on the cause or source of your pain, you may experience discomfort in a variety of different areas. Ask a doctor if you believe you may have injured your foot arch.
Diagnosis
In people with flat feet, the instep of the foot comes in contact with the ground when standing. To diagnose the problem, the health care provider will ask you to stand on your toes. If an arch forms,the flat foot is called flexible. You will not need any more tests or treatment. If the arch does not form with toe-standing (called rigid flat feet), or if there is pain, other tests may be needed, including a CT scan to look at the bones in the foot. MRI scan to look at the tendons in the foot. X-ray of the foot.
Non Surgical Treatment
There are many different causes of and treatments for flat foot. The most important part of treatment is determining the exact flat foot type on an individual basis, and doing so early on. The main objective is to become educated on the potential problems, so that you can stop them before they start. Conservative treatment is often successful if initiated early. The old adage "a stitch in time saves nine" definitely applies to the human body, hopefully more figuratively than literally. Do not ignore what your common sense and your body are telling you. Yes, you can live without an arch, but never neglect a symptomatic foot. If you neglect your feet, they will make you pay with every literal step you take.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be necessary in situations where the symptoms are likely to get worse over time, or when pain and instability cannot be corrected with external orthopedic devices. There are many types of surgical procedures, including cavus foot reconstruction, which can be performed to correct the foot and the ankle and restore function and muscle balance.
Prevention
Strap the arches into the anatomically correct positions with athletic tape and leave them like this for some time. If the fallen arches are an issue with the muscular structure, this may give the muscles an opportunity to strengthen. This is definitely not a fallen arches cure all the time but it can help prevent it more times than not. Ask a doctor or physical therapists to show you how to do this taping. Find shoes that fit. This may require that you get your foot measured and molded to ensure that the shoe will fit. Shoes that are too big, too tight or too short, may not directly cause the fallen arches, but they can assist with the damage to the area. These shoes should have thick cushioning inside and have plenty of room for your toes. Walk without shoes as much as possible. Shoes directly assist with weakening and distorting the arches of the feet so going without shoes can actually help strengthen your arches and prevent fallen arches. Walking on hard and bumpy surfaces barefooted makes the muscles in your feet strengthen in order to prevent injury. It is a coping mechanism by your body. Insert heel cups or insoles into the shoes that you wear the most. Many people wear uncomfortable shoes to work and these are the same shoes that cause their arches the most problems. Inserting the heel cups and insoles into these shoes can prevent fallen arches from occurring. Many people place these inserts into all their shoes to ensure support. Ask a medical professional, either your doctor or a physical therapist, about daily foot exercises that may keep the arches stronger than normal. Many times, you can find exercises and stretches on the Internet on various websites. Curling your toes tightly and rotating your feet will help strengthen your longitudinal arches. Relax your feet and shake them for a minute or so before you do any arch exercises. This will loosen the muscles in your feet that stay tight due to normal daily activities. Wear rigid soled sandals whenever possible to provide a strong support for your arches. Wooden soled sandals are the best ones if available. Walk or jog on concrete as much as you can. This will create a sturdy support for your arches. Running or walking in sandy areas or even on a treadmill, does not give rigid support. Instead, these surfaces absorb the step, offering no support for arches.
Stretching Exercises
Calf Stretching in Bed. As you may already know, the first few steps out of bed in the morning can be the worst of the day. Those first few steps can be enough to reaggravate your condition putting you into a cycle of inflammation and pain. The best way to help break that cycle is to stretch your calf before taking those first steps in the morning. When the muscles in your calf are tight, they pull on the heel bone, making your plantar fascia very taut and prone to injury. To help loosen those muscles, take a towel or belt and loop it around the ball of your foot. Keeping your leg straight, gently pull towards your body until you feel a stretch in the lower part of your leg. Hold that for 30 seconds and repeat up to 5 times before taking your first step out of bed. Plantar Fascia Stretching. Loosening up the tissues that are irritated probably makes sense to you, but you may not know how to do so. Luckily, there?s a very simple way. All you have to do is pull your toes up with your hand until you feel a stretch along the ball of your foot. You may feel the stretch anywhere from the ball of your foot to your heel. Holding this position for 30 seconds a few times can make a world of difference in your pain levels. Calf Stretching. I know, it probably seems like overkill, but stretching out the muscles in the lower leg is an integral step to recovery. There are two main muscles in the lower leg that attach to the heel, so we?ll work on stretching them both out. Stand against a wall and slide one leg back, pushing the heel down towards the floor (first picture). When you feel a stretch in the lower part of your leg, hold it for 30 seconds. After those 30 seconds are up, bend your knees until a deeper stretch is felt a bit lower in the leg (second photo). Again, hold this stretch for 30 seconds and repeat this until you?ve done it 3 times on each leg. Who doesn?t love a good massage? I suppose you could pay for someone to rub out the tissues in the bottom of your foot, but if you?re looking for a cheaper alternative, look no further than the humble tennis ball. Placing a tennis ball on the ground and gently rolling it under foot for a few minutes can help loosen up your plantar fascia, making it much less likely to become irritated. Put enough pressure on the ball to get a deep massage. You may feel some soreness, but back off if you feel any pain.Tennis Ball Massage While using the tennis ball is great for keeping things loose, sometimes it?s worth doing some icing at the same time for some inflammation control. Freezing a water bottle and rolling it under your foot for 10 minutes at the end of the day can be a very effective way to keep inflammation in check while staying loose. It might not be the most comfortable thing in the world, but ?Brrr? is better than ?Ouch? any day. One thing to keep in mind is that while these tips have been proven to work, they?re not an instant fix. It can take a few weeks of consistency with them before your pain levels begin to change. If you?re not seeing any improvement after making an honest effort, it may be time to look into some different treatment methods with your doctor such as formal PT, orthotics, a weight-loss plan, or others.